What is GST? GST Process, Types and Benefits
November 15, 2016 by Archi Bhatia
GST is a unified taxation system that is levied on the supply of goods and services in India. It is considered to be a comprehensive, multistage and destination based tax reform.
GST was brought into force by a constitutional amendment to deliver a uniform taxation law for Goods and services. It is dubbed as the Goods and Services Tax or GST that has now replaced various indirect tax laws that were applicable in India.
The New Tax Reform
GST tax reform was designed to eliminate the burden of double taxation on business across the country and provide single and streamlined process.
Unified Process
To put simply, Goods and Service Tax (GST) is one tax that will be levied on entire India on the supply of goods and services. The GST is going to subsume multiple taxes that are collected from suppliers, manufacturers and distributors such as VAT, service tax, CST, excise and additional excise duty.
Multistage Process
In a supply chain, an item goes through multiple changes of hands and GST is charged at every stage of the supply. For instance, when a manufacturer is buying raw material he will be levied GST on the raw material, and when he sells the finished product further to another buyer, the buyer will be charged GST; this process will continue until the ultimate consumer purchases the product.
Destination-Based
If the goods and services are produced in one state and a being sold in another, then the entire revenue will go to the state in which the product is sold and not the state producing the product.
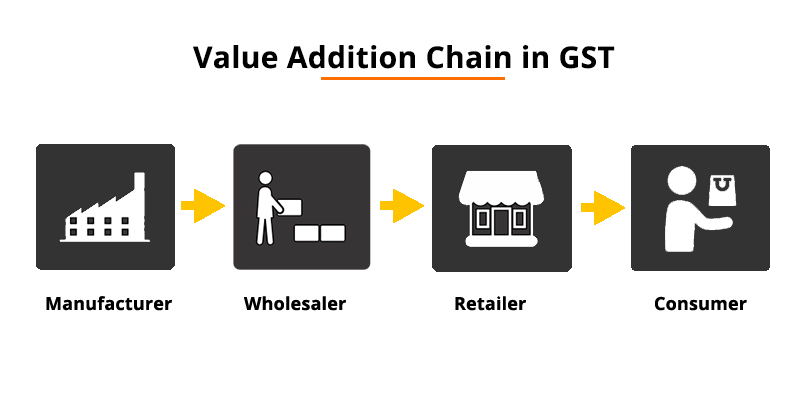
Value Addition
The goods and service tax is levied at every step of value creation. Simply put this means that final consumer will not bear the entire tax that is charged on the product.
For Instance, the manufacturer producing clothing material buys thread, dye colours and other material that eventually increases the value of the product. The manufacturer then sells the clothing material to a retailer who sells it further with his brand name to the ultimate consumers. Goods and Service tax is levied on all of the value addition and is ultimately added when the final sale to the consumer is made.
Type of GST
In India both the state uickcompany.in/articles/gst-filing">goods and services. For GST the constitution has provided a clear demarcation of powers and responsibility while collecting revenue from taxation.
CGST
The central GST or CGST is where the central government has the power to collect the revenue and applies to goods and services provided in a state.
SGST
SGST is a tax that is levied on all intrastate supplies of both Goods and Services by the state government and is governed by SGST act.
IGST
When the location of the supplier and the location of supply is in two different states then, in that case, IGST is collected by central government.
GST Registration Process
The taxpayers need to register themselves with the authorities, and the process can quickly be completed online by submitting key documents such as :
- Name of the business
- Pan card
- Aadhar card
- Contact Information (Email ID and Mobile No.)to receive OTP and TRN.
Then based on the Temporary Reference Number(TRN) application has to be completed and the applicant will receive Application Reference number through which they can check the status of their application.
Once verification is complete, the applicant receives notification on the registered number and e-mail id.
Eligibility
As per GST council, all those listed below need to register themselves:
- Existing taxpayers, Individuals that were filing taxes before implementation of GST.
- All the businesses that have a turnover of more than 20 lakh per annum.
- Individual supplying online information or providing database access to a place outside India.
GST Tax Rate
The GST council have finalised the tax rate for almost 1000 products and services in India. The tax slab was modified and significant changes have been brought under the following tariff heads on 10th November 2017.
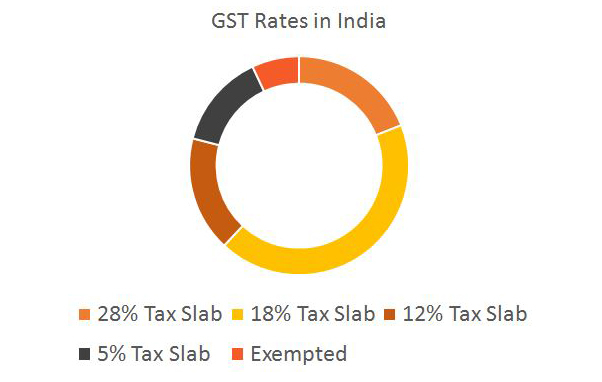
A summarised version of GST rate cuts for both goods and services are:
|
Products |
Tax Rate |
| Luxury products such as aerated drinks, cigarettes, premium cars and high-end motorcycle | 28% |
| Food items such as refined sugar, Pasta, Corn Flakes and processed foods, footwear above 500 and iron and steel products. | 18% |
| Services such as business class air travel, Dry fruits, Apparel above Rs. 1000 and Mobile Phones | 12% |
| Accessories available for differently able people, Goods for household necessities such as Transportation of goods and passengers. | 5% |
Goods and Services exempted from GST
All goods and services are enclosed to be taxed under GST except the following:
- Petroleum Products-Petroleum crude, Petrol, high-speed diesel, natural gas and aviation turbine fuel will be covered under the central sales tax.
- Electricity
- Property tax and stamp duty will be payable as are not covered under the GST
- Alcohol for human consumption has to pay central excise tax.
- Contraception
- Cosmetics and Accessories: Bindies, Sindoor, Bangles
GST Cess
It is an additional tax that is levied on the supply or distribution of certain goods that are notified by the government of India. States like Karnataka, Maharashtra, Gujrat and Haryana may face loss due to the implementation of GST and hence GST cess is levied to compensate the state's revenue.
Goods and Services that might attract GST Cess:
Procedure for filing returns
GST is believed to have a considerable impact on almost all the facets of business operations in the country, such as the pricing of the products and services, supply chain optimisation and tax compliance systems.
GSTR is completely an online process which all registered taxpayer have to file on monthly, quarterly and annually with the appropriate return forms. You need to share details of your business information like sales, purchases, tax collected and paid.
Benefits of GST
With the introduction of GST many of the consumer goods in India became costlier such as cinema tickets, insurance, food and Hotel charges but even with the following there are several benefits that are listed below:
- The entire process of registration, returns and payments are online, and hence the compliance procedure is straightforward and transparent for the filers. The uniformity of the tax has also made it easier for all in the compliance procedure as well.
- It has led to uniformity in the tax rate, and structure has brought tax neutrality all over India irrespective of the fact where you are practising or doing business.
- The minimum tax credit system ensures there is some value chain which would ensure that there is no cascading effect.
- After introducing GST, the government has let go of significant central and state taxes, which will increase the competitiveness and boost the Indian market.
Loans Through GSTIN
The government of India provide a loan based on GST returns filed by the GST number holder in the past financial years. The loan under this scheme can be obtained simply through GSTIN and the principle approval can be obtained within 60 minutes of filing application.
Penalties and Offences
Under following offences the structure of penalty is as follows:
1. Late Filing
The Individual or business filing GST registration late is charged a late fee of 200 Rs. Per day. However, in the case of late filing of IGST interest rate of 18% is charged and is calculated based on thetax that has to be paid to the government.
2. Not Filing Return
If a person doesn't file GST for 1 month will be liable to pay a hefty penalty. The offender will be liable to pay 10% of interest on the due tax as a penalty. The minimum amount of penalty levied is Rs.10,000.
3. In case of Fraud
In case the where a person or a business is in some way involved in Fraud or suppression of transaction then the person will be liable to pay penalty amount which could also lead to a jail term of 1 year to 5 years depending upon the amount of tax involved.