How to Copyright your Creative Work
October 26, 2018 by Akshara Bala
In India, Copyright Protection is automatic and no other formality is required. However, to further fortify protection, the copyright for the work can be registered to create bona-fide proof and prima facie evidence of ownership.
A Copyright is a type of Intellectual Property rights that protect the original creative works of an author that is created as a result of the intellectual ability and talent of the creator.
What Types of Creative Works are Protected by Copyright?
A copyright protects most original creative works that are expressed in a tangible form. These include:
- Literary works – Such as books, journals, publications, blogs, song lyrics, even computer coding and film scripts.
- Artistic works – Paintings, photographs, sculptures, architectural drawings, graphic art, etc.
- Cinematographic work – Including films, motion graphic films, videos, choreographed works, drama, theatrical work and parodies.
- Musical Compositions – The composition of music expressed in musical notes, both vocal and instrumental. Musical compositions don’t have to be necessarily written to be protected.
- Sound recordings: The recording of a musical composition using a specific recording medium and with the help of artists can also be copyrighted.
All these works have to be view in depth to understand the applicability of copyright. For instance, songs are protected by two copyrights, one for the musical composition and another for the sound recording.
When Does Copyright Protection Come into Force?
A copyright is created immediately when the work is created and expressed in a tangible medium such as paper, film, or computer chip.
Under the Indian Copyright law, protection is automatic and no formality is required to gain such basic protection except for the creation of the work.
Ownership of the Copyright
The copyright is the intellectual property of the rightful owner of the creative work. The owner has the exclusive rights of reproduction, performance, public display, adaptation, modification and translation of the work.
The owner of the copyright could either be:
- The original creator
- Someone who has been assigned the copyright
- Someone who has commissioned the work from the original creator and has also been licensed the copyright
It’s important to note that, merely paying a creator for the creation of the work will not lead to the transfer of copyrights. The creator must also transfer the rights to you.
For instance, if you have purchased a painting, the copyright for the painting isn’t attached to the cost of the work. The artist would still hold the copyright to the painting unless he/she transfers it to you.
What is the Copyright Registration Process?
Although copyright registration is automatic, registration would create a stronger legal base for your copyright in an event of copyright infringement.
Only the true ‘final draft’ of the work has to be submitted for registration, any additions to the work after registration will not be included as a part of the registered copyright.
Step 1: Filing the Copyright Application
The application for registration of copyrights can be done either physically or via the online application process.
- The application should be submitted with the requisite fees, and along with the supporting documents like the final draft of the work and identity proof
- Once the application has been submitted successfully, a diary number is generated for the applicant to check the status of the application.
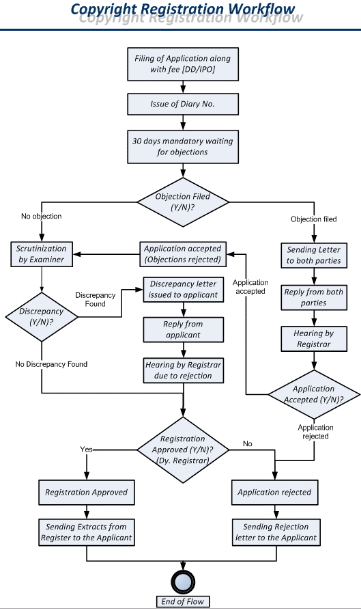
Step 2: Examination of the Application
Once the application has been submitted, a mandatory waiting period of 30 days is to be observed as an opportunity for third-parties to raise objections. Once the 30-day waiting period
of eclipses, the application goes to several stages of examination. The flowchart below describes the process which the application goes through.
Step 3: Copyright Registration
The registration of the copyright depends on the Copyright Registrar. Once the application is approved and registered, the applicant can exercise his additional rights such as seeking damages on infringement, etc.